
What are UTI’s? Urinary Tract Infections
Do you… Frequently or urgently need to urinate Often only pass small amounts of urine Have Pain or burning sensation when urinating These can be symptoms of urinary tract infections. There
Psoriasis is a long -term autoimmune disease which affects the skin, resulting patches of red, scaly skin, which are typically extremely itchy and painful. This condition affects 2% of Australia’s population and conditions can vary from localized in one area, to complete body coverage. Common problem areas for psoriasis are: knees, elbows, scalp, torso, palms, and the soles of feet.
It is known to have a varying or fluctuating course, where the disease improves and then worsens, and is thought to be incurable but not untreatable.
Psoriasis can occur in anyone from babies, to elderly people, but the most common age of diagnosis is in early adult years.
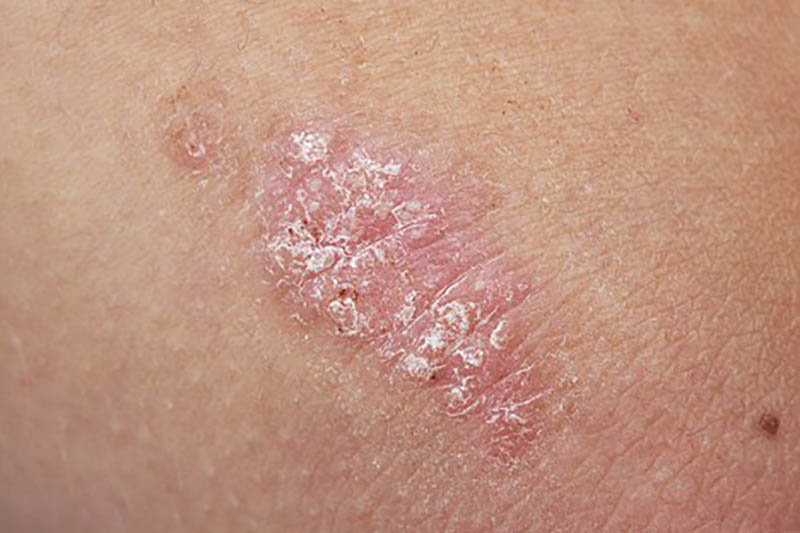
This chronic disease is caused the rapid increase in the production of skin cells, which, when these skin cells reach the surface and die, their sheer volume causes a build-up, and raised red plaques covered in white scales appear. This increase in the production of skin cells is caused by the immune system being ‘triggered’ by environmental factors, resulting in the production of excess inflammatory chemicals.
Studies show that people with psoriasis are more susceptible to illnesses such as diabetes, heart disease, and psoriasis sufferers are between 10 and 30% more likely to develop psoriatic arthritis.

Do you… Frequently or urgently need to urinate Often only pass small amounts of urine Have Pain or burning sensation when urinating These can be symptoms of urinary tract infections. There
Disclaimer – Our intent is not to diagnosis but to offer information on therapy choices and practitioners. Information on this site is intended general educational purposes only. Any statements made are carefully referenced and any information, products or services discussed are not intended to diagnose, cure, treat or prevent any disease or illness. Please consult a healthcare practitioner before making a choice.